OUR SERVICES
Cataracts, glaucoma, intravitreal drug administration for macular and retinal diseases, eyelid surgery
Cataracts are an eye disease that is usually age-related, but can also have other causes, and which causes a steady decline in vision. To treat cataracts, surgery is necessary to replace the cloudy lens with an artificial lens.
Untreated glaucoma can lead to blindness due to destruction of the optic nerve. Glaucoma is treated with medication or surgery with the aim of reducing intraocular pressure.
Intravitreal drug administration is a method of delivering drugs into the eye so that they can act directly at the site of action.
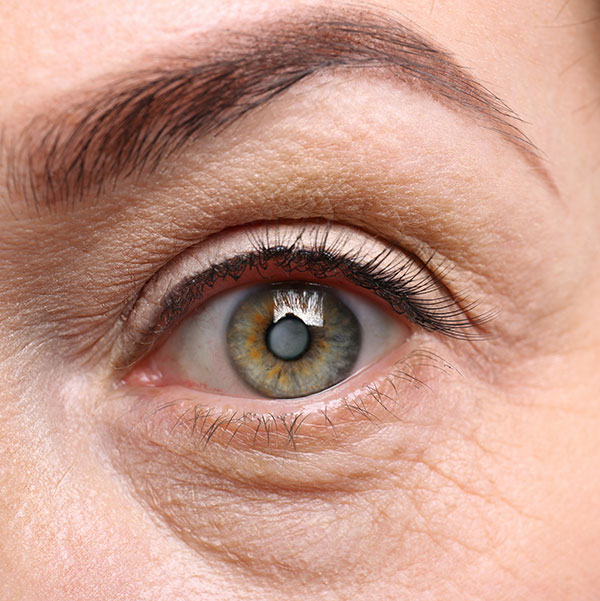
Eyelid surgery
Blepharoplasty, eyelid tumours, styes, xanthelasma, ectropion/entropion.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis under local anaesthesia.